Cloud Computing Intro
- Cloud is the abbreviation for cloud computing and stands for storage, computing power, or software products that can be used even though they are not available on the local computer.
- Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Cloud Service Provider (CSP)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS All-in-one
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Microsoft Azure
Types of Cloud
Cloud-based deployment (Public)
- owner is the CSP
- Run all parts of the application in the cloud
- Migrate existing applications to the cloud
- Design and build new applications in the cloud
On-premises deployment (Private cloud deployment)
- owner is the company
- Deploy resources by using virtualization and resource management tools
- Increase resource utilization by using application management and virtualization technologies
Hybrid deployment
- = public + private: owner is the company
- Connect cloud-based resources to on-premises infrastructure
- Integrate cloud-based resources with legacy IT applications
Types of Cloud service models
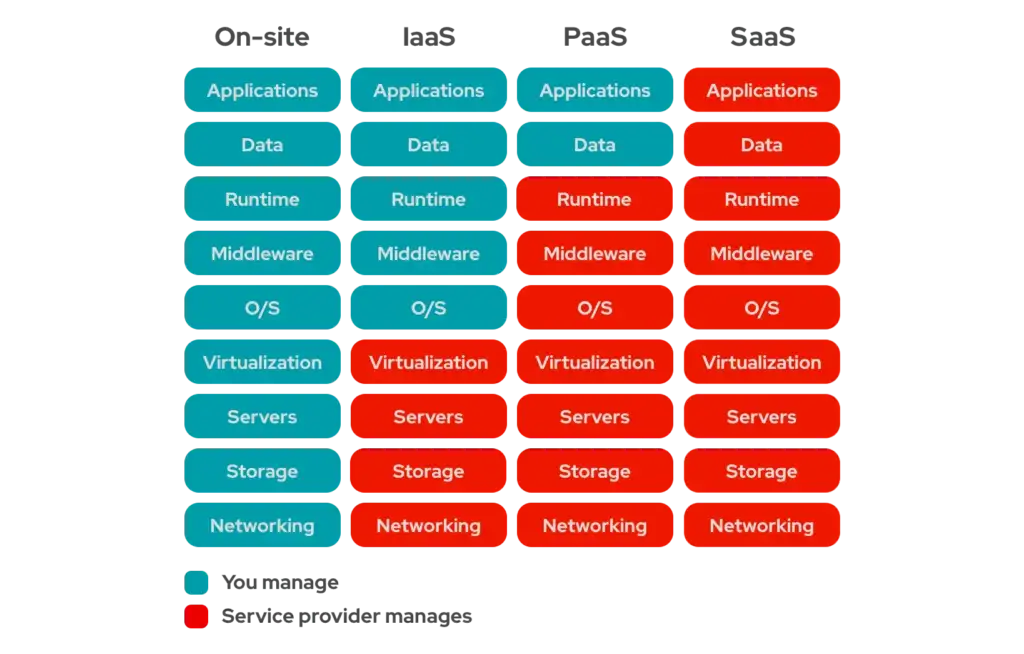
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- e.g. Dropbox
Advantages of cloud computing
- Pay as you go
- Trade upfront expense for variable expense
- Not having to invest in technology resources before using them
- Benefit from massive economies of scale
- The aggregated cloud usage from a large number of customers results in lower pay-as-you-go prices
- Stop guessing capacity
- Accessing services on-demand helps to prevent excess or limited capacity
- Increase speed and agility
- Realize cost savings
- Go global in minutes